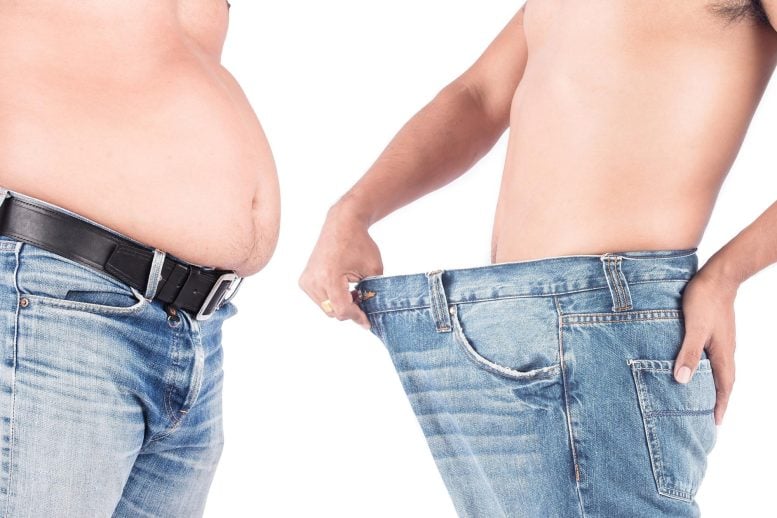
After two years, individuals who bear metabolic and bariatric surgical procedure obtain weight reduction that’s about 5 occasions better than with non-surgical approaches.
Semaglutide and tirzepatide have turn into a number of the most talked-about drugs in trendy weight reduction care. Semaglutide is the energetic ingredient in Ozempic, a drug initially used for sort 2 diabetes that can be extensively identified for serving to folks shed some pounds.
Tirzepatide is a more recent injectable remedy in the identical broader class of metabolic medicine and has drawn consideration for its results on urge for food and blood sugar. Each are taken as weekly injections and are a part of a gaggle known as GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Even with all the thrill, a brand new head-to-head real-world research suggests these drugs might not ship weight reduction on the identical scale as bariatric surgical procedure over the long run. Researchers reported that sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass had been related to about five-times extra weight reduction than weekly injections of the GLP-1 receptor agonists semaglutide or tirzepatide, on the finish of two years. The findings had been just lately offered on the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgical procedure (ASMBS) 2025 Annual Scientific Assembly.
Weight Loss Outcomes After Two Years
The evaluation, led by researchers at NYU Langone Well being and NYC Well being + Hospitals, discovered a serious hole between the 2 approaches. After two years, sufferers who underwent one of many bariatric procedures misplaced a mean of 58 kilos. By comparability, sufferers who obtained a GLP-1 prescription for at the very least six months misplaced a mean of 12 kilos (24% whole weight reduction vs. 4.7%).
Staying on the remedy longer appeared to assist, however it nonetheless didn’t shut the hole. Sufferers on steady GLP-1 remedy for a full yr misplaced extra weight than these handled for at the very least six months, but their outcomes remained far under these seen in surgical procedure sufferers (7% whole weight reduction).
Actual-World Outcomes Versus Medical Trials
“Medical trials present weight reduction between 15% to 21% for GLP-1s, however this research means that weight reduction in the true world is significantly decrease, even for sufferers who’ve energetic prescriptions for a complete yr. We all know as many as 70% of sufferers might discontinue remedy inside one yr,” mentioned lead research creator Avery Brown, MD, a surgical resident at NYU Langone Well being. “GLP-1 sufferers might have to regulate their expectations, adhere extra carefully to remedy or go for metabolic and bariatric surgical procedure to attain desired outcomes.”
The researchers carried out a retrospective comparative effectiveness evaluation utilizing real-world digital medical information from NYU Langone Well being and NYC Well being + Hospitals. The research included sufferers with a physique mass index (BMI) of at least 35 who either underwent bariatric surgery (sleeve gastrectomy or Roux en-Y gastric bypass) or were prescribed injectable semaglutide or tirzepatide between 2018 and 2024.
To ensure a fair comparison, the team adjusted for differences in age, BMI, and comorbidities using average treatment effect weighting. They then evaluated outcomes across a total of 51,085 patients treated with either GLP-1 medications or surgical procedures.
Future Directions and Treatment Optimization
“In future studies we will aim to identify what healthcare providers can do to optimize GLP-1 outcomes, identify which patients are better treated with bariatric surgery versus GLP-1s, and determine the role out-of-pocket costs play in treatment success,” said study senior author and bariatric surgeon Karan R. Chhabra, MD, MSc, Assistant Professor of Surgery and Population Health, NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
About 12% of Americans say they have ever taken a GLP-1 drug, including 6% who say they are currently in treatment. A recent study found that more than half of patients with overweight or obesity (53.6%) discontinued GLP-1 therapy within one year (53.6%), a number that grows to 72.2% by two years. Meanwhile, utilization of metabolic and bariatric surgery remains exceedingly low. According to the ASMBS, more than 270,000 metabolic and bariatric procedures were performed in 2023, which represents only about 1% of those who meet eligibility requirements based on BMI.
Expert Perspective on Weight-Loss Treatments
“While both patient groups lose weight, metabolic and bariatric surgery is much more effective and durable,” said ASMBS President Ann M. Rogers, MD, FACS, FASMBS, who was not involved in the study. “Those who get insufficient weight loss with GLP-1s or have challenges complying with treatment due to side effects or costs, should consider bariatric surgery as an option or even in combination.”
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the prevalence of obesity and severe obesity is 40.3% and 9.4%, respectively. Studies show the disease can weaken or impair the body’s immune system and cause chronic inflammation and increase the risk of scores of other diseases and conditions including cardiovascular disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
Meeting: American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting
The study was supported by NYU CTSA grant KL2 TR001446 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
Follow us on Google and Google News.
















