The findings might allow earlier detection and therapy for folks affected by the intense eye situation.
A analysis crew on the College of Missouri has made a discovery that would pave the way in which for figuring out a biomarker to detect and deal with a serious eye illness a lot earlier. The situation, referred to as glaucoma, ranks among the many prime causes of everlasting blindness in older adults.
Glaucoma damages the retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons, that are the nerve fibers in the back of the attention that ship visible indicators to the mind. When these nerves deteriorate, imaginative and prescient loss happens. Though present remedies might help decrease strain inside the attention, they haven’t been in a position to cease or shield RGCs from harm. Creating therapies that safeguard these cells and stop their degeneration stays one of many biggest challenges in glaucoma care.
On the College of Missouri, researcher Pawan Singh is working to alter that. His purpose is to determine biomarkers that may reveal the presence of glaucoma early on and to develop new neuroprotective remedies that protect imaginative and prescient and sluggish the illness’s development.
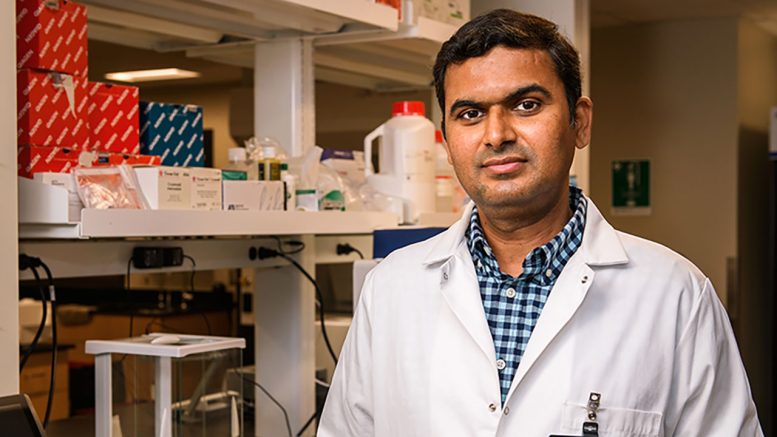

In a latest research, his crew found that glaucoma sufferers have much less of two tiny molecules — agmatine and thiamine — within the clear fluid on the entrance of the attention, in comparison with these with out glaucoma. Singh has recognized that these molecules, referred to as metabolites, may very well be potential biomarkers that may very well be noticed to detect the illness early.
Towards Earlier Detection
“In a number of instances, folks don’t discover out they’ve glaucoma till they’re older and their eye strain is elevated,” Singh, an assistant professor within the Faculty of Medication, stated. “Our long-term purpose is to see if medical doctors might someday do a easy blood take a look at to test for these biomarkers. If they will, hopefully they may have the ability to catch the illness a lot earlier, earlier than imaginative and prescient loss happens, so sufferers can obtain therapy sooner.”
These two metabolites, agmatine and thiamine, might additionally make for potential glaucoma remedies. In one in every of his latest pre-clinical research, Singh discovered that agmatine and thiamine have neuroprotective potential and might help shield RGCs from harm and lack of visible operate. This implies these molecules may assist cease or decelerate the development of imaginative and prescient loss, making them attainable candidates for future neuroprotective therapy for glaucoma as eye drops or dietary supplements.
“Mizzou’s spectacular analysis infrastructure and our collaborative crew assist make this analysis attainable,” Singh stated. “Whereas extra work must be achieved, the attention medical doctors I’ve spoken to right here at Mizzou are very enthusiastic about this analysis, so I’m proud and looking forward to the longer term.”
Reference: “Metabolomic Profiling of Aqueous Humor From Glaucoma Sufferers Identifies Metabolites With Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Potential in Mice” by Monu Monu, Bhoj Kumar, Rahmat Asfiya, Nariman Nassiri, Vaama Patel, Shibandri Das, Sarah Syeda, Mamta Kanwar, Vivian Rajeswaren, Bret A. Hughes, Mark S. Juzych, Akhil Srivastava, Ashok Kumar and Pawan Kumar Singh, Could 2025, Investigative Ophthalmology & Visible Science.
DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.28
By no means miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
Comply with us on Google, Discover, and News.