Researchers on the College of Stuttgart have created an “optical sieve” able to detecting minute nanoplastic particles. Functioning very like a take a look at strip, this innovation is designed to offer a brand new analytical device for environmental and well being analysis.
Researchers from the College of Stuttgart in Germany and the College of Melbourne in Australia have launched a easy solution to analyze very small nanoplastic particles in environmental samples. The strategy depends on an ordinary optical microscope and a newly designed take a look at strip referred to as the optical sieve. The findings are reported in Nature Photonics.
“The test strip can serve as a simple analysis tool in environmental and health research,” explains Prof. Harald Giessen, Head of the 4th Physics Institute of the University of Stuttgart. “In the near future, we will be working toward analyzing nanoplastic concentrations directly on site. But our new method could also be used to test blood or tissue for nanoplastic particles.”
Nanoplastics as a danger to humans and the environment
Plastic waste ranks among the most urgent global challenges of the 21st century. It contaminates oceans, rivers, and beaches, and microplastics have been found in living organisms. Until recently, researchers have mainly examined larger fragments of plastic. Evidence now points to an even more concerning threat: nanoplastic particles.
These particles are far smaller than the width of a human hair, form as bigger pieces of plastic break down, and cannot be seen with the naked eye. At sub-micrometer sizes, they can also pass through biological barriers, including the skin and the blood-brain barrier.
Color changes make tiny particles visible
Because of the small particle size, their detection poses a particular challenge. As a result, there are not only gaps in our understanding of how particles affect organisms but also a lack of rapid and reliable detection methods.
In collaboration with a research group from Melbourne in Australia, researchers at the University of Stuttgart have now developed a novel method that can quickly and affordably detect such small particles. Color changes on a special test strip make nanoplastics visible in an optical microscope and allow researchers to count the number of particles and determine their size.
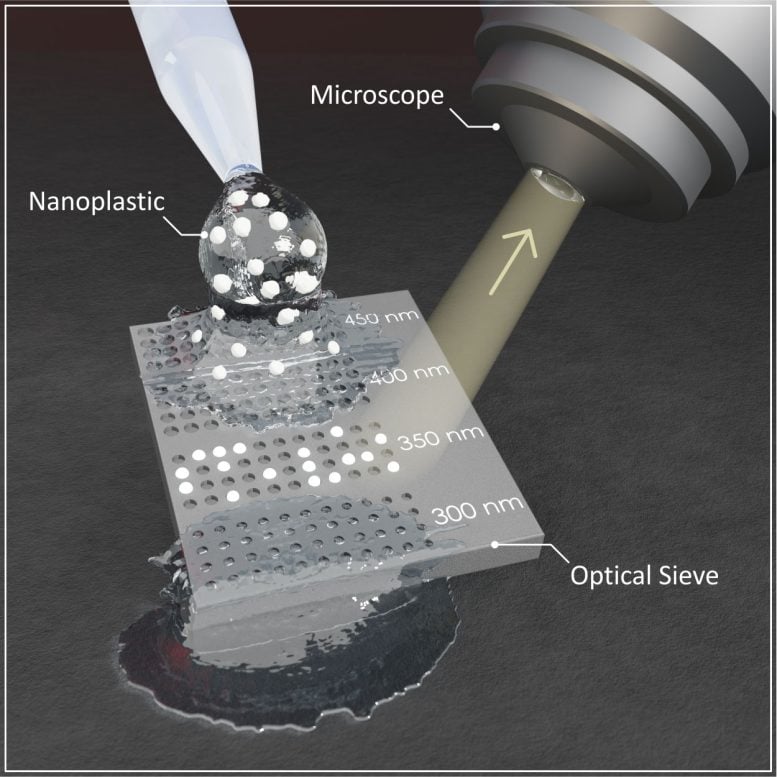
“Compared with conventional and widely used methods such as scanning electron microscopy, the new method is considerably less expensive, does not require trained personnel to operate, and reduces the time required for detailed analysis,” explains Dr. Mario Hentschel, Head of the Microstructure Laboratory at the 4th Physics Institute.
Optical sieve instead of expensive electron microscope
The “optical sieve” uses resonance effects in small holes to make the nanoplastic particles visible. A study on optical effects in such holes was first published by the research group at the University of Stuttgart in 2023. The process is based on tiny depressions, known as Mie voids, which are etched into a semiconductor substrate.
Depending on their diameter and depth, the holes interact characteristically with the incident light. This results in a bright color reflection that can be seen in an optical microscope. If a particle falls into one of the indentations, its color changes noticeably. One can therefore infer from the changing color whether a particle is present in the void.
“The test strip works like a classic sieve,” explains Dominik Ludescher, PhD student and first author of the publication in “Nature Photonics”. Particles ranging from 0.2 to 1 µm can thus be examined without difficulty. “The particles are filtered out of the liquid using the sieve in which the size and depth of the holes can be adapted to the nanoplastic particles, and subsequently, the resulting color change can be detected. This allows us to determine whether the voids are filled or empty.”
Number, size, and size distribution of particles can be determined
The novel detection method used can do even more. If the sieve is provided with voids of different sizes, only one particle of a suitable size will collect in each hole.
“If a particle is too large, it won’t fit into the void and will be simply flushed away during the cleaning process,” says Ludescher. “If a particle is too small, it will adhere poorly to the well and will be washed away during cleaning.” In this way, the test strips can be adapted so that the size and number of particles in each individual hole can be determined from the reflected color.
Synthesized environmental samples examined
For their measurements, the researchers used spherical particles of various diameters. These are available in aqueous solutions with specific nanoparticles. Because real samples from bodies of water with known nanoparticle concentrations are not yet available, the team produced a suitable sample themselves.
The researchers used a water sample from a lake that contained a mixture of sand and other organic components and added spherical particles in known quantities. The concentration of plastic particles was 150 µg/ml. The number and size distribution of the nanoplastic particles were also determined for this sample using the “optical sieve.”
Can be used like a test strip
“In the long term, the optical sieve will be used as a simple analysis tool in environmental and health research. The technology could serve as a mobile test strip that would provide information on the content of nanoplastics in water or soil directly on site,” explains Hentschel.
The team is now planning experiments with nanoplastic particles that are not spherical. The researchers also plan to investigate whether the process can be used to distinguish between particles of different plastics. They are also particularly interested in collaborating with research groups that have specific expertise in processing real samples from bodies of water.
Reference: “Optical sieve for nanoplastic detection, sizing and counting” by D. Ludescher, L. Wesemann, J. Schwab, J. Karst, S. B. Sulejman, M. Ubl, B. O. Clarke, A. Roberts, H. Giessen and M. Hentschel, 8 September 2025, Nature Photonics.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01733-x
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.