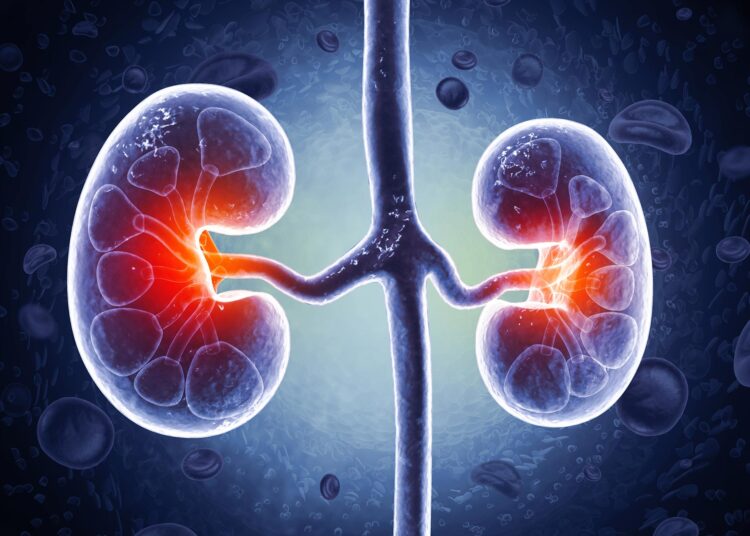
Hundreds of thousands of kidney sufferers may gain advantage from early detection and prevention on account of the breakthrough made by scientists on the CRCHUM.
In a groundbreaking achievement, researchers on the CRCHUM, the hospital analysis heart affiliated with Université de Montréal, have recognized a sort of microRNA that may safeguard small blood vessels and assist keep kidney perform following extreme damage.
This discovery holds vital promise for the greater than 4 million Canadians dwelling with continual renal failure, in addition to thousands and thousands of sufferers worldwide, by providing new potentialities for earlier detection and prevention of the illness.
Till now, there had been no reliable biomarker to evaluate the situation of those delicate capillaries or to information focused methods geared toward defending kidney perform.
Discovery of miR-423-5p as a biomarker
Findings printed in JCI Perception reveal that the microRNA generally known as miR-423-5p reveals sturdy potential as a blood-based biomarker for evaluating kidney microvascular well being.
The examine was co-authored by Université de Montréal medical professors Marie-Josée Hébert and Héloïse Cardinal, who maintain the Shire Chair in Nephrology, Renal Transplantation and Regeneration, alongside Hébert’s analysis affiliate Francis Migneault.
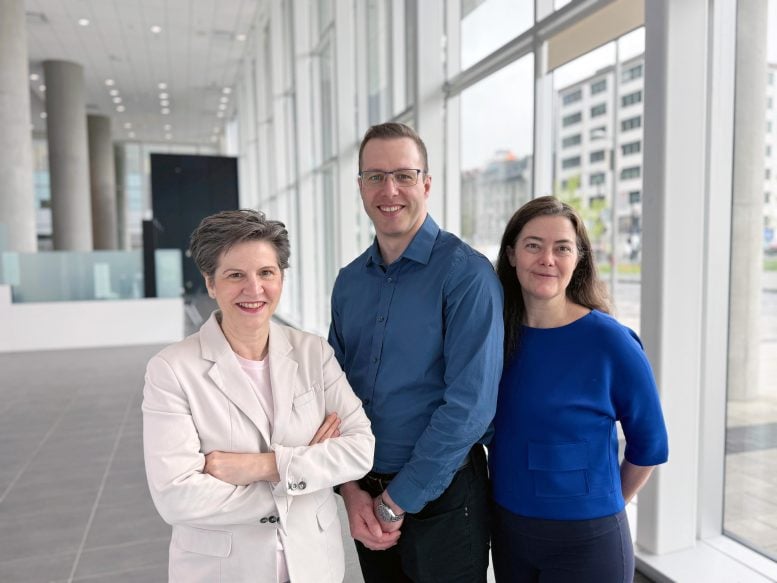

Their analysis focuses on the decline of peritubular capillaries, a key indicator of continual renal failure.
These minute vessels, discovered within the kidneys by the thousands and thousands, are accountable for eradicating waste from the blood whereas delivering oxygen and vitamins important for kidney perform.
Dangers and potential functions in sufferers
Kidney harm that happens when blood move is briefly reduce off after which restored can lead to the lack of small blood vessels, considerably impairing the organ’s means to perform correctly.
“In individuals who have acquired a transplant, if kidney perform is severely altered, the kidney’s survival is threatened,” stated Hébert, a nephrology-transplant doctor and UdeM’s outgoing vice-rector for analysis, discovery, creation, and innovation.
“Utilizing this biomarker, a check might be developed to guage the standing of the small blood vessels a lot earlier,” she stated. “Medical doctors in hospitals might then higher consider the microvascular well being of higher-risk sufferers.
“These might embody aged sufferers or these present process surgical procedures throughout which blood move is briefly stopped, as is the case for organ transplants or cardiovascular interventions.”
Of mice and… 51 transplant recipients
“We first noticed fluctuating ranges of miR-423-5p microRNA within the blood of mice with acute kidney accidents,” stated Migneault, the examine’s first creator. “These outcomes have been then confirmed in 51 transplant recipients who participated within the CHUM kidney transplant biobank.”
Due to this biomarker, medical groups might verify whether or not their interventions enhance or diminish the well being of small blood vessels.
“However what’s actually unimaginable is that by injecting this microRNA into mice with kidney accidents, we have been in a position to protect the small blood vessels and restrict the harm achieved to the kidneys,” stated Migneault.
Whereas direct injection into the kidney is a clinically possible technique throughout a transplant, to guard the remaining small blood vessels, the CRCHUM scientists at the moment are centered on different methods to move the microRNA, or doubtless a microRNA cocktail, to the kidney.
Doubtlessly helpful for different sufferers
By way of prevention, a check primarily based on this miR-423-5p microRNA might be helpful for sufferers with cardiac failure, pulmonary failure, or sure neurodegenerative ailments.
“For these medical situations, the lack of small blood vessels performs a key function, due to the affiliation with regular or accelerated growing old,” stated Hébert. “Our discovery might, due to this fact, have a big affect on the well being of all Canadians.”
For these with pulmonary failure, a number of analysis tasks are in progress beneath Emmanuelle Brochiero, a researcher and head of the Immunopathology analysis theme on the CRCHUM.
It might even be attainable, utilizing the CHUM’s organic materials biobank, to find out if current drugs, administered after a kidney transplant to deal with one other situation, affect small blood vessel well being, added Hébert.
Reference: “Endothelial extracellular vesicle miR-423-5p regulates microvascular homeostasis and renal perform after ischemia-reperfusion damage” by Francis Migneault, Hyunyun Kim, Alice Doreille, Shanshan Lan, Alexis Gendron, Marie-Hélène Normand, Annie Karakeussian Rimbaud, Martin Dupont, Isabelle Bourdeau, Éric Bonneil, Julie Turgeon, Sylvie Dussault, Pierre Thibault, Mélanie Dieudé, Éric Boilard, Alain Rivard, Héloïse Cardinal and Marie-Josée Hébert, 22 Might 2025, JCI Perception.
DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.181937
This analysis was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Well being Analysis, the Shire Chair in Nephrology, Renal Transplantation and Regeneration at Université de Montréal, the Fondation J.-Louis Lévesque, the Canadian Donation and Transplantation Analysis Program, the Fonds de recherche du Québec—Santé, and the Pure Sciences and Engineering Analysis Council of Canada. It was supported by the molecular pathology and animal core facility groups.
Dr. Hébert, Dr. Cardinal, Francis Migneault and the members of their group wish to thank the CHUM sufferers for his or her participation within the CHUM kidney transplant biobank, in addition to the medical and analysis workers who make sure the continued existence of the biobank.
By no means miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.